Agglutinate comes from "ad+glue" means to cause to adhere as with glue, or to clump together.
Agglutinin, is any substance that is capable of causing agglutination of a particular antigen.
In blood, antibodies are agglutinins, and red blood cells (of the wrong blood group), bacteria form the antigen.
There is an auto immune disease in which circulating abnormal antibodies, usually IgM, directed against one's own red blood cells are abnormally present.
This causes hemolysis, anemia, and it is autoimmune (autoimmune hemolytic anemia)
There is maximum action at temperatures lower than body temperature and that's why it's called cold agglutinins
(This is against warm agglutinins in Warm Antibody Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia, in which there is a more complex interaction through which IgG antibodies make macrophages bite off the membrane of RBCs turning them into spherocytes which are destroyed in spleen. Maybe since there is more number of interactions taking place, it's more efficient in higher temperatures (like chemical reactions) )
Tuesday, June 26, 2012
Thursday, June 7, 2012
Sugarless and sugared diabetes
di·a·be·tes/ˌdīəˈbētēz/
Noun:
A disorder of the metabolism causing
excessive thirst and the production
of large amounts of urine.
Latin mellitus, honey-sweet
Latin insipidus, insipid
in·sip·id
adj.
1. Lacking flavor or zest; not tasty.
Latin in-, not; + Latin sapidus, savory (from sapere, to taste; from
Latin sapor, flavor)
--
Diabetes mellitus is
Type 1 (Compare with primary) : Insulin depended. That is, due to
insulin deficiency.
Type 2 (Secondary, not directly due to insulin deficiency) : Insulin
independent. Due to lifestyle.
Noun:
A disorder of the metabolism causing
excessive thirst and the production
of large amounts of urine.
Latin mellitus, honey-sweet
Latin insipidus, insipid
in·sip·id
adj.
1. Lacking flavor or zest; not tasty.
Latin in-, not; + Latin sapidus, savory (from sapere, to taste; from
Latin sapor, flavor)
--
Diabetes mellitus is
Type 1 (Compare with primary) : Insulin depended. That is, due to
insulin deficiency.
Type 2 (Secondary, not directly due to insulin deficiency) : Insulin
independent. Due to lifestyle.
How To Study Reaction Cycles
Biochemistry is full of reactions and cascades of them.
And how to study it, is simple.
Have the idea what changes into what.
Glycolysis is glucose to pyruvate. There are 6 carbons, it must become
3, and the energy released should be trapped too. This is not easily
achieved in a single step. And so, there are multiple reactions.
Phosphorylation makes the compound easy to break. and so on..
You have a keto bond. You need to make this a C-N bond. Enter an
aspartate moiety and it's thrown out as fumarate and what will remain is
an amine! and so on..
And how to study it, is simple.
Have the idea what changes into what.
Glycolysis is glucose to pyruvate. There are 6 carbons, it must become
3, and the energy released should be trapped too. This is not easily
achieved in a single step. And so, there are multiple reactions.
Phosphorylation makes the compound easy to break. and so on..
You have a keto bond. You need to make this a C-N bond. Enter an
aspartate moiety and it's thrown out as fumarate and what will remain is
an amine! and so on..
Sunday, June 3, 2012
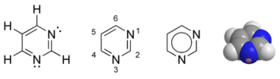
IUPAC numbering of purines and pyrimidines
If you've been like me, you had a hard time remembering the numbering of purines and pyrimidines and an even harder time thinking why they are numbered so. No more hard times :D
The article here says two simple rules for numbering a heterocyclic ring:
That's pyrimidine structure for you
And that's purine, both from wikipedia.
If you've got doubt on me, GUArdian Angels are PURe and TWO wINGED
(Guanine and Adenosine are Purines and Two Ringed)
As is evident, the Nitrogen atoms are being given the smallest numbering. Then, the carbons that are shared between cycles are given the smallest numbers. And then, the double bonds!
The article here says two simple rules for numbering a heterocyclic ring:
- Hetero atoms should have the lowest possible numbers.
- Carbon atoms which are shared by two rings should follow the lowest
possible numbers.
That's pyrimidine structure for you
And that's purine, both from wikipedia.
If you've got doubt on me, GUArdian Angels are PURe and TWO wINGED
(Guanine and Adenosine are Purines and Two Ringed)
As is evident, the Nitrogen atoms are being given the smallest numbering. Then, the carbons that are shared between cycles are given the smallest numbers. And then, the double bonds!
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)